X-rays and health – separating facts from myths and explaining what’s true
X-rays, or radiographic examinations, are a topic that often sparks strong emotions and controversy. In an age of increasing online information, it can be difficult to separate facts from myths. Is X-ray imaging truly harmful to your health, or are the concerns exaggerated? In this article, we take a closer look at this issue from multiple perspectives, analyzing both the benefits and the potential risks associated with radiological examinations. You will learn about the latest medical findings as well as expert recommendations. Understanding how X-rays work and how they are used in diagnostics is essential for making informed decisions about your health. Get ready to uncover the facts and debunk the myths that may influence your perception of this important area of medicine.
Introduction to x-ray imaging (RTG)
X-rays, also known as radiographic examinations, are a diagnostic and therapeutic technique that uses X-ray radiation to create images of the inside of the body. It is one of the most commonly used tools in medicine, helping doctors diagnose a wide range of conditions and monitor patients’ health. Despite its widespread use, X-ray imaging remains a topic of controversy, mainly due to concerns about potential side effects of radiation exposure. You may also be interested in radiation Y: What you need to know about its impact on health and the environment.
In the age of the internet, where information is available at your fingertips, it is easy to come across conflicting reports about X-rays. There is no shortage of articles that raise alarm about its harmfulness, as well as those that downplay the risks. For this reason, understanding the true nature of X-rays and their impact on health is crucial for patients who want to make informed decisions about their treatment.
In this article, we will look at both the benefits and the risks associated with X-ray examinations. We will explain how this technology works, discuss its historical origins, and present the latest discoveries in the field. We will also address popular myths and facts surrounding X-rays and show how the risks associated with their use can be minimized. At the end of the article, we will provide practical recommendations for patients to help them better understand and safely utilize this technology.
How does an x-ray examination work?
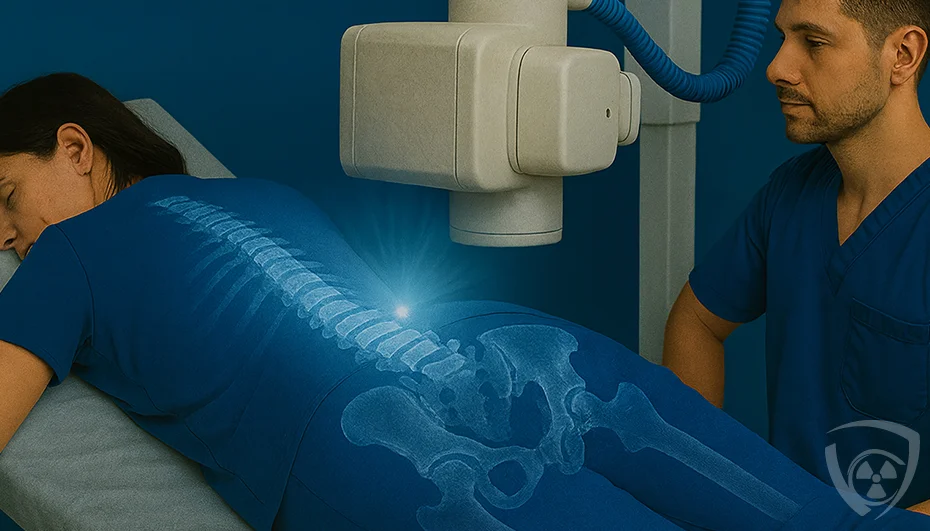
An X-ray examination uses X-ray radiation to create images of the inside of the body. This radiation is a form of electromagnetic energy that passes through soft tissues, such as skin and muscles, but is largely absorbed by denser structures like bones. As a result, bones appear as bright areas on X-ray images, while soft tissues appear darker.
The process begins by positioning the patient between the radiation source and the image detector. X-ray radiation passes through the patient’s body and reaches the detector, which records an image of the internal structures. Depending on diagnostic needs, images may be taken from various angles to obtain the most complete view of the area being examined.
This technology is highly precise and allows for quick, painless acquisition of detailed images. It is an invaluable tool in medical diagnostics, helping physicians detect fractures, tumors, infections, and many other conditions. Moreover, modern X-ray equipment is increasingly advanced, offering enhanced image quality while simultaneously reducing the radiation dose, which contributes to greater patient safety.
The history and development of x-ray technology
The first X-ray image was taken in 1895 by German physicist Wilhelm Roentgen, whose name became the basis for the term “Roentgen radiation” (X-rays). This discovery revolutionized medicine, allowing doctors to look inside the human body for the first time without the need for surgery. For his groundbreaking achievement, Roentgen received the first Nobel Prize in Physics in 1901.
Over the following decades, X-ray technology continued to evolve. New imaging methods were introduced, such as computed tomography (CT), which enables the creation of three-dimensional images of the body’s interior. The development of digital image detectors also transformed the way data is stored and analyzed, making the diagnostic process faster and more efficient.
Modern X-ray systems are equipped with advanced radiation protection features that minimize exposure risks for both patients and medical staff. Thanks to these innovations, X-ray examinations have become a safer and more reliable diagnostic method, widely used across various fields of medicine—from orthopedics to dentistry.
Potential health risks associated with x-ray examinations
Although X-ray examinations are widely used and considered safe, certain health risks related to exposure to X-ray radiation cannot be completely ruled out. This type of radiation is a form of ionizing energy, which has the ability to damage cellular DNA and, over the long term, may contribute to the development of cancer.
One of the main risks associated with X-rays is the potential increase in cancer risk. While the radiation doses used in medical diagnostics are relatively low, repeated exposure to radiation can elevate the likelihood of cancer development. Children and pregnant women are particularly sensitive to radiation, which is why special precautions are taken for these groups.
Another potential risk is tissue damage. Although rare, high doses of radiation can cause skin burns and damage to internal organs. In clinical practice, such incidents are extremely uncommon, and modern X-ray equipment is designed to minimize the likelihood of these events.
Facts about x-ray radiation
X-ray radiation is a form of ionizing electromagnetic radiation widely used in medical diagnostics. One of the most important facts about X-rays is that the radiation doses used in diagnostic examinations are generally very low. For example, a standard chest X-ray delivers a dose comparable to the natural background radiation we receive over the course of a few days.
Moreover, modern technologies allow for significant dose reduction while maintaining high image quality. As a result, X-ray examinations are becoming increasingly safe, enabling patients to benefit from diagnostics without fearing excessive radiation exposure.
It is also worth noting that X-ray radiation is used not only for diagnostics but also for treatment. Radiation therapy — the use of ionizing radiation to treat cancer — is one of the key methods in oncology. In such cases, radiation doses are much higher than those used in diagnostics, but the therapeutic benefits far outweigh the potential risks.
Myths about x-rays and their debunking
There are many myths surrounding X-rays that can mislead patients and create unnecessary fear. One of the most common myths is the belief that every X-ray examination is highly harmful to health. In reality, as mentioned earlier, the radiation doses used in diagnostics are very low and do not pose a significant health risk—especially when examinations are performed according to medical guidelines.
Another widespread myth is that X-ray radiation is always dangerous for pregnant women. Although pregnant women should indeed avoid unnecessary radiation exposure, in situations where an X-ray examination is essential for the health of the mother or the baby, doctors take all possible precautions to minimize the risk. Special protective shields (fixed and mobile shields, protective materials) and imaging techniques can significantly reduce the amount of radiation reaching the fetus.
A further myth is the belief that X-ray examinations can cause infertility. There is no scientific evidence indicating that the radiation doses used in medical diagnostics can lead to infertility. In fact, X-ray radiation levels are far too low to cause such effects, particularly when examinations are performed by qualified medical personnel.
When Is an x-ray necessary?
X-ray examinations are indispensable in many clinical situations where fast and accurate diagnosis is crucial for further patient care. One of the most common uses of X-rays is trauma diagnostics. X-ray images allow physicians to quickly assess bone fractures, joint dislocations, and other injuries, which is invaluable in emergency situations.
X-rays are also essential in diagnosing lung diseases such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, and lung cancer. Chest X-rays enable rapid detection of pathological changes, allowing treatment to begin early. In dentistry, X-rays are widely used to evaluate the condition of teeth, roots, and the bones of the jaw and mandible, which is crucial for planning dental procedures.
Another important use of X-rays is monitoring treatment progress. For example, in cancer patients, regular X-ray examinations can help assess the effectiveness of therapy and detect potential recurrences. In such cases, the benefits of X-ray examinations far outweigh the potential risks associated with radiation exposure.
Alternatives to x-ray examinations
Although X-rays are an extremely useful diagnostic tool, there are other imaging methods that may be used as alternatives depending on the patient’s needs. One of the most common alternatives is ultrasound (USG), which uses sound waves to create images of the inside of the body. Ultrasound is particularly valuable in diagnosing abdominal organ diseases, assessing the heart, and monitoring pregnancy.
Another alternative is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to produce detailed images of the body. MRI is frequently used in diagnosing neurological and orthopedic conditions, as well as evaluating soft tissues. Unlike X-rays, MRI does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safe option for patients who require frequent imaging.
Computed tomography (CT) is another alternative that, like X-rays, uses ionizing radiation but enables the creation of three-dimensional images of the body. CT is especially useful in diagnosing injuries, cancers, and assessing the condition of internal organs. Although CT involves a higher radiation dose than standard X-ray imaging, it provides exceptionally detailed images that may be critical for an accurate diagnosis.
How to minimize risk during x-ray examinations?
To minimize the risks associated with exposure to X-ray radiation, both patients and medical staff should follow several fundamental guidelines. First and foremost, X-ray examinations should be performed only when truly necessary. Physicians should carefully assess the benefits and risks of the examination to ensure it is justified.
Another important precaution is the use of appropriate protective shielding. Patients should be equipped with lead aprons and shields (personal protective equipment – PPE) that protect the most sensitive areas of the body, such as the thyroid, reproductive organs, and the abdomen in the case of pregnant women. Medical staff should also use radiological protective gear and maintain an adequate distance from the radiation source during the procedure.
It is also worth paying attention to modern technologies that help reduce radiation dose. Many contemporary X-ray systems are equipped with automatic dose adjustment features that tailor radiation levels to diagnostic needs, allowing for high-quality images with minimal exposure. Patients should feel free to ask their doctors about the availability of such technologies and the possibility of using alternative imaging methods when appropriate.
Summary and recommendations for patients
X-ray examinations are an invaluable diagnostic tool that plays a key role in modern medicine. They enable doctors to quickly and accurately diagnose a wide range of conditions and monitor treatment progress. Although X-ray radiation carries some level of risk, modern technologies and proper safety measures help minimize this risk and ensure patient safety.
It is important for patients to be aware of both the benefits and potential risks associated with X-ray examinations. They should always consult their doctors and ask questions about the necessity of the examination and available alternatives. When an X-ray is required, patients should ensure that appropriate protective measures and modern dose-reducing technologies are being used.
Making informed decisions about one’s health is essential for every patient. Understanding how X-rays work, as well as their advantages and limitations, allows individuals to better manage their health and use available diagnostic methods safely and responsibly. Remember: knowledge and education are the best tools for protecting our health.